ommerce is the activity of buying and selling goods and services, and it encompasses a broad range of activities and disciplines. Here’s a quick rundown of the basics:
1. Definition and Scope
- Commerce involves all activities related to the trade of goods and services, including the distribution, marketing, and sales processes.
- It plays a key role in the economy by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.

2. Key Components
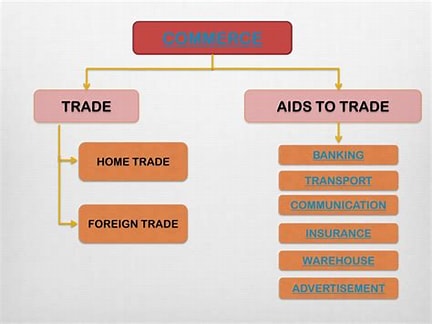
- Trade: The actual exchange of goods and services for money.
- Distribution: The process of getting products from manufacturers to consumers.
- Marketing: Activities that promote and sell products or services, including advertising, sales, and market research.
- Finance: Managing money, including investments, funding, and financial planning.
- Logistics: Planning and managing the flow of goods and services, including warehousing and transportation.
3. Types of Commerce
- E-Commerce: Buying and selling goods and services over the internet.
- Retail: Selling products directly to consumers.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
4. Business Models
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third party (e.g., eBay).
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals selling products or offering services to businesses (e.g., freelance work).
5. Key Processes
- Procurement: Acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
- Sales: The process of selling goods or services.
- Customer Service: Support provided to customers before, during, and after a purchase.
- Accounting: Recording and analyzing financial transactions to manage business finances.
6. Regulations and Ethics
- Regulations: Laws and guidelines that businesses must follow, which vary by country and industry.
- Ethics: Principles that guide behavior in commerce, including fair trade practices, transparency, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Economic Impact
- Job Creation: Commerce drives employment in various sectors such as retail, logistics, and finance.
- Economic Growth: By facilitating trade and investment, commerce contributes to overall economic development.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced concepts and practices in commerce. If you have any specific areas you’d like to dive deeper into, feel free to ask!
ommerce is the activity of buying and selling goods and services, and it encompasses a broad range of activities and disciplines. Here’s a quick rundown of the basics:
1. Definition and Scope
- Commerce involves all activities related to the trade of goods and services, including the distribution, marketing, and sales processes.
- It plays a key role in the economy by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
2. Key Components
- Trade: The actual exchange of goods and services for money.
- Distribution: The process of getting products from manufacturers to consumers.
- Marketing: Activities that promote and sell products or services, including advertising, sales, and market research.
- Finance: Managing money, including investments, funding, and financial planning.
- Logistics: Planning and managing the flow of goods and services, including warehousing and transportation.
3. Types of Commerce
- E-Commerce: Buying and selling goods and services over the internet.
- Retail: Selling products directly to consumers.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
4. Business Models
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third party (e.g., eBay).
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals selling products or offering services to businesses (e.g., freelance work).
5. Key Processes
- Procurement: Acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
- Sales: The process of selling goods or services.
- Customer Service: Support provided to customers before, during, and after a purchase.
- Accounting: Recording and analyzing financial transactions to manage business finances.
6. Regulations and Ethics
- Regulations: Laws and guidelines that businesses must follow, which vary by country and industry.
- Ethics: Principles that guide behavior in commerce, including fair trade practices, transparency, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Economic Impact
- Job Creation: Commerce drives employment in various sectors such as retail, logistics, and finance.
- Economic Growth: By facilitating trade and investment, commerce contributes to overall economic development.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced concepts and practices in commerce. If you have any specific areas you’d like to dive deeper into, feel free to ask!ommerce is the activity of buying and selling goods and services, and it encompasses a broad range of activities and disciplines. Here’s a quick rundown of the basics:
1. Definition and Scope
- Commerce involves all activities related to the trade of goods and services, including the distribution, marketing, and sales processes.
- It plays a key role in the economy by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
2. Key Components
- Trade: The actual exchange of goods and services for money.
- Distribution: The process of getting products from manufacturers to consumers.
- Marketing: Activities that promote and sell products or services, including advertising, sales, and market research.
- Finance: Managing money, including investments, funding, and financial planning.
- Logistics: Planning and managing the flow of goods and services, including warehousing and transportation.
3. Types of Commerce
- E-Commerce: Buying and selling goods and services over the internet.
- Retail: Selling products directly to consumers.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
4. Business Models
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third party (e.g., eBay).
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals selling products or offering services to businesses (e.g., freelance work).
5. Key Processes
- Procurement: Acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
- Sales: The process of selling goods or services.
- Customer Service: Support provided to customers before, during, and after a purchase.
- Accounting: Recording and analyzing financial transactions to manage business finances.
6. Regulations and Ethics
- Regulations: Laws and guidelines that businesses must follow, which vary by country and industry.
- Ethics: Principles that guide behavior in commerce, including fair trade practices, transparency, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Economic Impact
- Job Creation: Commerce drives employment in various sectors such as retail, logistics, and finance.
- Economic Growth: By facilitating trade and investment, commerce contributes to overall economic development.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced concepts and practices in commerce. If you have any specific areas you’d like to dive deeper into, feel free to ask!ommerce is the activity of buying and selling goods and services, and it encompasses a broad range of activities and disciplines. Here’s a quick rundown of the basics:
1. Definition and Scope
- Commerce involves all activities related to the trade of goods and services, including the distribution, marketing, and sales processes.
- It plays a key role in the economy by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
2. Key Components
- Trade: The actual exchange of goods and services for money.
- Distribution: The process of getting products from manufacturers to consumers.
- Marketing: Activities that promote and sell products or services, including advertising, sales, and market research.
- Finance: Managing money, including investments, funding, and financial planning.
- Logistics: Planning and managing the flow of goods and services, including warehousing and transportation.
3. Types of Commerce
- E-Commerce: Buying and selling goods and services over the internet.
- Retail: Selling products directly to consumers.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
4. Business Models
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third party (e.g., eBay).
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals selling products or offering services to businesses (e.g., freelance work).
5. Key Processes
- Procurement: Acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
- Sales: The process of selling goods or services.
- Customer Service: Support provided to customers before, during, and after a purchase.
- Accounting: Recording and analyzing financial transactions to manage business finances.
6. Regulations and Ethics
- Regulations: Laws and guidelines that businesses must follow, which vary by country and industry.
- Ethics: Principles that guide behavior in commerce, including fair trade practices, transparency, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Economic Impact
- Job Creation: Commerce drives employment in various sectors such as retail, logistics, and finance.
- Economic Growth: By facilitating trade and investment, commerce contributes to overall economic development.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced concepts and practices in commerce. If you have any specific areas you’d like to dive deeper into, feel free to ask!ommerce is the activity of buying and selling goods and services, and it encompasses a broad range of activities and disciplines. Here’s a quick rundown of the basics:
1. Definition and Scope
- Commerce involves all activities related to the trade of goods and services, including the distribution, marketing, and sales processes.
- It plays a key role in the economy by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
2. Key Components
- Trade: The actual exchange of goods and services for money.
- Distribution: The process of getting products from manufacturers to consumers.
- Marketing: Activities that promote and sell products or services, including advertising, sales, and market research.
- Finance: Managing money, including investments, funding, and financial planning.
- Logistics: Planning and managing the flow of goods and services, including warehousing and transportation.
3. Types of Commerce
- E-Commerce: Buying and selling goods and services over the internet.
- Retail: Selling products directly to consumers.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
4. Business Models
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third party (e.g., eBay).
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals selling products or offering services to businesses (e.g., freelance work).
5. Key Processes
- Procurement: Acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
- Sales: The process of selling goods or services.
- Customer Service: Support provided to customers before, during, and after a purchase.
- Accounting: Recording and analyzing financial transactions to manage business finances.
6. Regulations and Ethics
- Regulations: Laws and guidelines that businesses must follow, which vary by country and industry.
- Ethics: Principles that guide behavior in commerce, including fair trade practices, transparency, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Economic Impact
- Job Creation: Commerce drives employment in various sectors such as retail, logistics, and finance.
- Economic Growth: By facilitating trade and investment, commerce contributes to overall economic development.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced concepts and practices in commerce. If you have any specific areas you’d like to dive deeper into, feel free to ask!ommerce is the activity of buying and selling goods and services, and it encompasses a broad range of activities and disciplines. Here’s a quick rundown of the basics:
1. Definition and Scope
- Commerce involves all activities related to the trade of goods and services, including the distribution, marketing, and sales processes.
- It plays a key role in the economy by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
2. Key Components
- Trade: The actual exchange of goods and services for money.
- Distribution: The process of getting products from manufacturers to consumers.
- Marketing: Activities that promote and sell products or services, including advertising, sales, and market research.
- Finance: Managing money, including investments, funding, and financial planning.
- Logistics: Planning and managing the flow of goods and services, including warehousing and transportation.
3. Types of Commerce
- E-Commerce: Buying and selling goods and services over the internet.
- Retail: Selling products directly to consumers.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
4. Business Models
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third party (e.g., eBay).
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals selling products or offering services to businesses (e.g., freelance work).
5. Key Processes
- Procurement: Acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
- Sales: The process of selling goods or services.
- Customer Service: Support provided to customers before, during, and after a purchase.
- Accounting: Recording and analyzing financial transactions to manage business finances.
6. Regulations and Ethics
- Regulations: Laws and guidelines that businesses must follow, which vary by country and industry.
- Ethics: Principles that guide behavior in commerce, including fair trade practices, transparency, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Economic Impact
- Job Creation: Commerce drives employment in various sectors such as retail, logistics, and finance.
- Economic Growth: By facilitating trade and investment, commerce contributes to overall economic development.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced concepts and practices in commerce. If you have any specific areas you’d like to dive deeper into, feel free to ask!ommerce is the activity of buying and selling goods and services, and it encompasses a broad range of activities and disciplines. Here’s a quick rundown of the basics:
1. Definition and Scope
- Commerce involves all activities related to the trade of goods and services, including the distribution, marketing, and sales processes.
- It plays a key role in the economy by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
2. Key Components
- Trade: The actual exchange of goods and services for money.
- Distribution: The process of getting products from manufacturers to consumers.
- Marketing: Activities that promote and sell products or services, including advertising, sales, and market research.
- Finance: Managing money, including investments, funding, and financial planning.
- Logistics: Planning and managing the flow of goods and services, including warehousing and transportation.
3. Types of Commerce
- E-Commerce: Buying and selling goods and services over the internet.
- Retail: Selling products directly to consumers.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
4. Business Models
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third party (e.g., eBay).
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals selling products or offering services to businesses (e.g., freelance work).
5. Key Processes
- Procurement: Acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
- Sales: The process of selling goods or services.
- Customer Service: Support provided to customers before, during, and after a purchase.
- Accounting: Recording and analyzing financial transactions to manage business finances.
6. Regulations and Ethics
- Regulations: Laws and guidelines that businesses must follow, which vary by country and industry.
- Ethics: Principles that guide behavior in commerce, including fair trade practices, transparency, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Economic Impact
- Job Creation: Commerce drives employment in various sectors such as retail, logistics, and finance.
- Economic Growth: By facilitating trade and investment, commerce contributes to overall economic development.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced concepts and practices in commerce. If you have any specific areas you’d like to dive deeper into, feel free to ask!
ommerce is the activity of buying and selling goods and services, and it encompasses a broad range of activities and disciplines. Here’s a quick rundown of the basics:
1. Definition and Scope
- Commerce involves all activities related to the trade of goods and services, including the distribution, marketing, and sales processes.
- It plays a key role in the economy by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
2. Key Components
- Trade: The actual exchange of goods and services for money.
- Distribution: The process of getting products from manufacturers to consumers.
- Marketing: Activities that promote and sell products or services, including advertising, sales, and market research.
- Finance: Managing money, including investments, funding, and financial planning.
- Logistics: Planning and managing the flow of goods and services, including warehousing and transportation.
3. Types of Commerce
- E-Commerce: Buying and selling goods and services over the internet.
- Retail: Selling products directly to consumers.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
4. Business Models
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third party (e.g., eBay).
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals selling products or offering services to businesses (e.g., freelance work).
5. Key Processes
- Procurement: Acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
- Sales: The process of selling goods or services.
- Customer Service: Support provided to customers before, during, and after a purchase.
- Accounting: Recording and analyzing financial transactions to manage business finances.
6. Regulations and Ethics
- Regulations: Laws and guidelines that businesses must follow, which vary by country and industry.
- Ethics: Principles that guide behavior in commerce, including fair trade practices, transparency, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Economic Impact
- Job Creation: Commerce drives employment in various sectors such as retail, logistics, and finance.
- Economic Growth: By facilitating trade and investment, commerce contributes to overall economic development.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced concepts and practices in commerce. If you have any specific areas you’d like to dive deeper into, feel free to ask!ommerce is the activity of buying and selling goods and services, and it encompasses a broad range of activities and disciplines. Here’s a quick rundown of the basics:
1. Definition and Scope
- Commerce involves all activities related to the trade of goods and services, including the distribution, marketing, and sales processes.
- It plays a key role in the economy by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
2. Key Components
- Trade: The actual exchange of goods and services for money.
- Distribution: The process of getting products from manufacturers to consumers.
- Marketing: Activities that promote and sell products or services, including advertising, sales, and market research.
- Finance: Managing money, including investments, funding, and financial planning.
- Logistics: Planning and managing the flow of goods and services, including warehousing and transportation.
3. Types of Commerce
- E-Commerce: Buying and selling goods and services over the internet.
- Retail: Selling products directly to consumers.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
4. Business Models
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Transactions between businesses and individual consumers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Transactions between individual consumers, often facilitated by a third party (e.g., eBay).
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals selling products or offering services to businesses (e.g., freelance work).
5. Key Processes
- Procurement: Acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
- Sales: The process of selling goods or services.
- Customer Service: Support provided to customers before, during, and after a purchase.
- Accounting: Recording and analyzing financial transactions to manage business finances.
6. Regulations and Ethics
- Regulations: Laws and guidelines that businesses must follow, which vary by country and industry.
- Ethics: Principles that guide behavior in commerce, including fair trade practices, transparency, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Economic Impact
- Job Creation: Commerce drives employment in various sectors such as retail, logistics, and finance.
- Economic Growth: By facilitating trade and investment, commerce contributes to overall economic development.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced concepts and practices in commerce. If you have any specific areas you’d like to dive deeper into, feel free to ask!
